There are topics that how we could extend layer2 over layer3 for DC interconnect. And there are various options to achieve this.
- VPLS (Virtual Private LAN Service)
- Q-in-Q
- OTV (Overlay Transport Virtulization)
- VXLAN (VMWare VTEP)
- EVI (Ethernet Virtual Interconnect)
Option 1 and 2 is kind of outdated since they’re create a larger broadcast domain. OTV is Cisco proprietary protocol depends on GRE, and there is a nice write up for OTV by Brain OTV. VXLAN is popular now which mainly becos of the boosting VMWare, and there are alot articles about this. Here i will focus on the EVI which is announced by HP.
Advantage:
- Extend up to 4096 vlans over
- Broadcast domain will not extend over
- Throughput can go-up to line-rate
Disadvantage:
- No such thing call qos-preclassify
- As we use GRE, so EVI won’t load-balance between the two links
- There are no way to monitor the throughput of virtual link (ELINK)
Let’s go into the configurations, and make sure the same vlan are created on both end
【Router A】
interface Tunnel 1 mode evi # Create the EVI interface
evi network-id 1 # Create the EVI unique identifier
source 192.168.250.55 # Define the GRE Source
keepalive 20 2 # send 2 keep packets in 20s interval
evi-isis extend-vlan 3700 # Define the VLAN to go across
evi neighbor-discovery server enable # enable the discovery in Server mode
Enable the EVI function on the physical interface
evi enable
【Router B】
interface Tunnel 1 mode evi # Create the EVI interface
evi network-id 1 # Create the EVI unique identifier
source 192.168.250.35 # Define the GRE Source
keepalive 20 2 # send 2 keep packets in 20s interval
evi-isis extend-vlan 3700 # Define the VLAN to go across
evi neighbor-discovery client enable 192.168.250.55 # enable client mode
Enable the EVI function on the physical interface
evi enable
By now, the EVI should be up and running
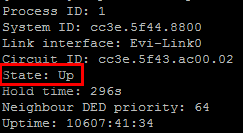
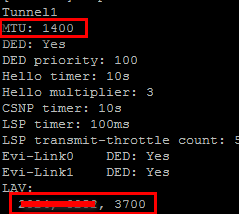
And you will be able to see that VLAN permitted and MTU that allowed to go across the EVI
So there is a database running on both routers, and will store the local mac address and remote mac address, here is how EVI control the broadcast domain. Once the router saw a broadcast frame that includes the destination mac address in the local database then it will not forward the broadcast over.
Conclude: EVI generally Okay, but there are disadvantages to use it. I am not sure whether OTV and VXLAN will have the same issue or not, probably you guys could comment.

Pingback: Resumo HP EVI | Comutadores
Hi,
did you have to filter any of FHRPs over EVI tunnel ? If yes, can you explain how pls?
LikeLike
Nope, not necessarily….. EVI tunneled layer2 over, not even layer3 yet
LikeLike
EN una red con protocolo IGP, realizo reconocimiento y estado de interfaces por señalizan ldp estática (TE CD LDP) o Dinamico (TE RSVP). Como EVI puede realizar descubrimiento de red y controlar el QoS?…QoS es por DSCP?
LikeLike
Hi Manuel, thanks for your comment, but i dont understand spanish, assume you’re asking the evi support for QoS, my answer is i dont think you could apply a QoS to the EVI interface ….
LikeLike